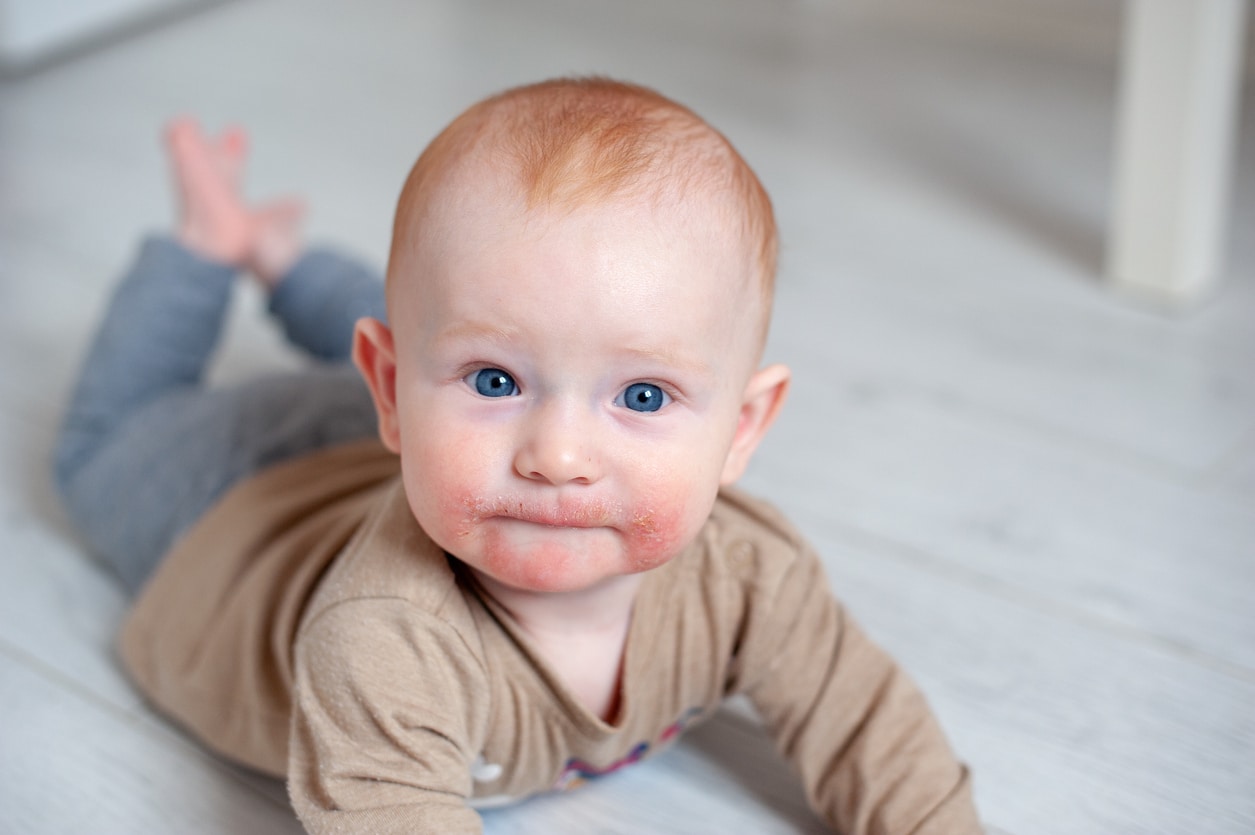
Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema Treatment in Frisco, TX
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema:
1 in 10 Americans has atopic dermatitis, and over 31 million Americans have some form of eczema. Eczema refers to a group of skin conditions that cause inflamed, irritated, and itchy skin. It includes nummular eczema, contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and dyshidrotic eczema.
Symptoms range from excessively dry, itchy skin to painful, itchy rashes that cause sleepless nights and interfere with school and work. Many people with atopic dermatitis also have asthma, food allergies, hay fever, and other environmental allergies.
At Rodgers Dermatology, we create a caring and comfortable environment to help you look—and feel—your very best. We have extensive experience treating sensitive skin. For fast relief, please contact us now and set up an appointment.
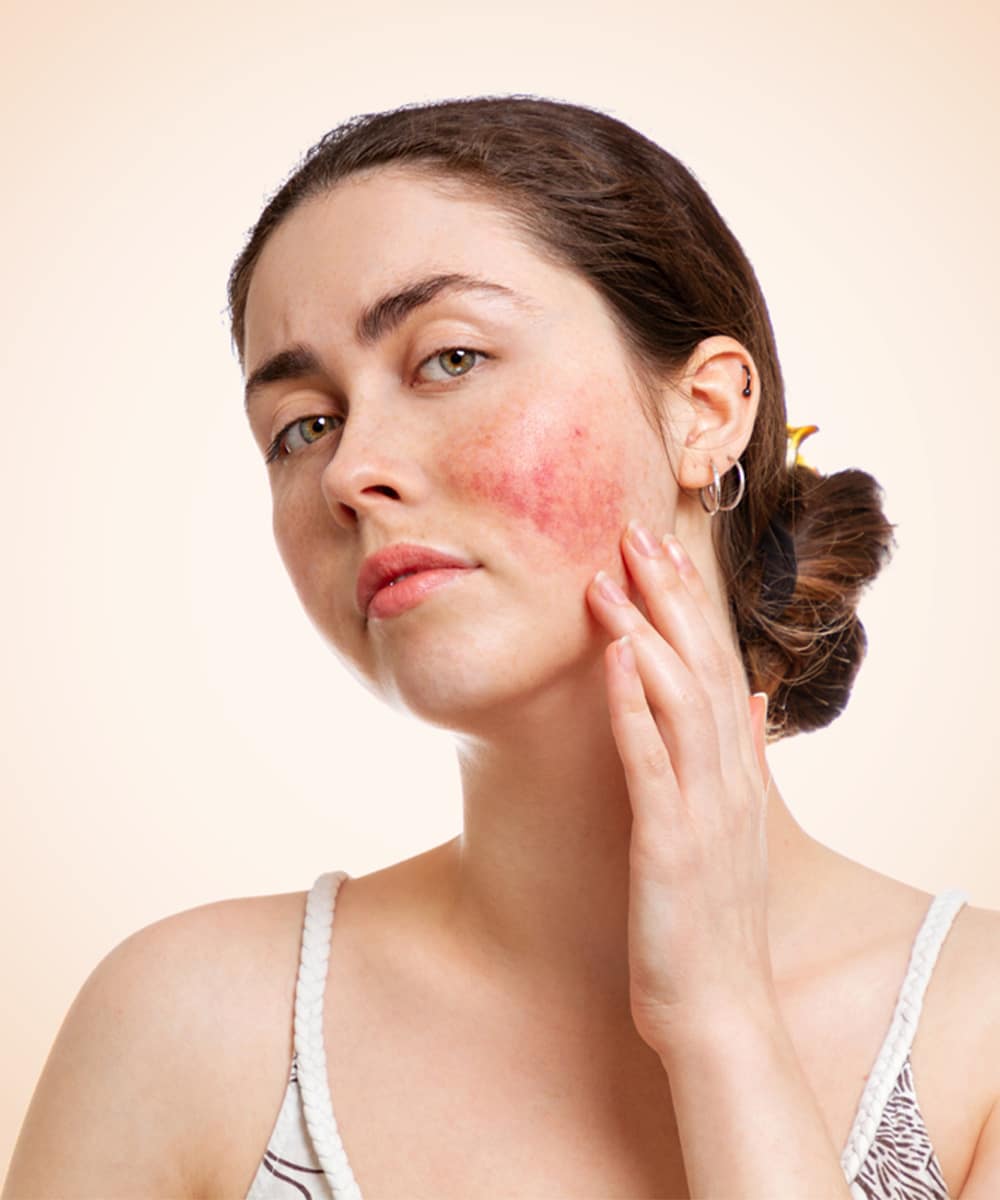

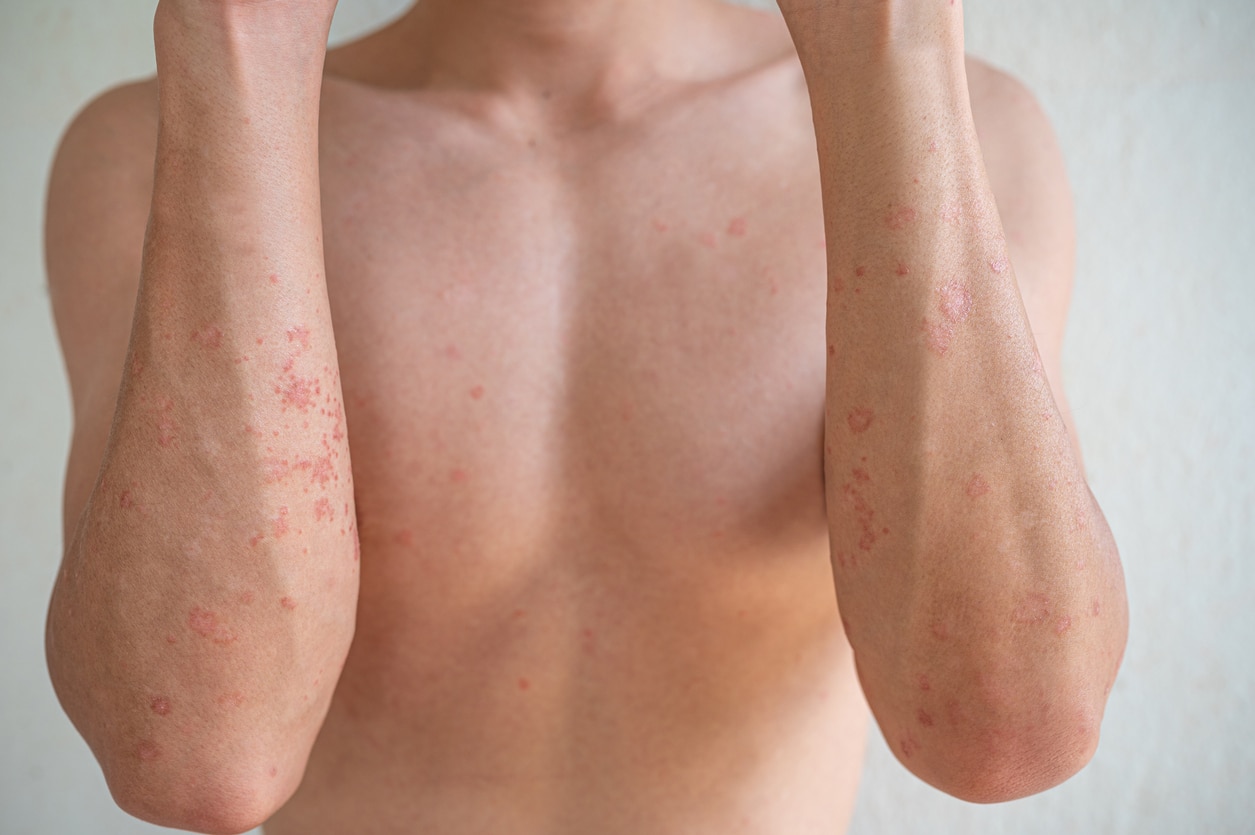
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis a.k.a Eczema
You can develop atopic eczema at any age, although it usually first appears in childhood. Signs and symptoms of this inflammatory skin condition include:
- Red inflamed skin
- Patches of dry, scaly skin
- Intense itching
- Swelling
- Crusting or oozing skin
- Painful lesions and fluid-filled tiny blisters
Note: On brown or black skin, eczema may appear gray or purple instead of red.
Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema Treatment Options
There is no cure for eczema, but there are various treatments that can help manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
Creams, Ointments, & Moisturizers
Topical steroids can be used to reduce inflammation and itching of the skin. They can be applied once or twice a day to the affected areas, depending on the strength and prescription. Topical steroids can help control mild to moderate eczema flare-ups and prevent them from worsening. The specific choice of topical steroid depends on the severity and location of eczema, as well as the age and weight of the person. They should only be used under medical supervision.
Similarly, calcineurin inhibitors are medications that help suppress the immune system’s response that causes eczema symptoms. They can be applied once or twice a day to the affected areas, depending on the prescription. Eczema happens when your immune system is overactive. Calcineurin inhibitors help control this by telling your T cells to calm down, thus reducing inflammation. Calcineurin inhibitors can help control moderate to severe eczema flare-ups that do not respond well to topical steroids. Calcineurin inhibitors come in two types: tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel). They are available as creams or ointments. They are especially useful for treating eczema on sensitive areas, such as the face or neck.
Moisturizers, also known as emollients, can also be applied to hydrate and protect the skin. They can also prevent water loss and enhance the skin barrier.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are medications that help block the action of histamine, a chemical that causes itching and inflammation in allergic reactions. They can be taken orally or applied topically to the itchy areas, depending on the type and dose of antihistamine. Antihistamines can help relieve itching and improve sleep quality in patients suffering from eczema symptoms.
Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema FAQs
To Find Relief from Severe Eczema Now, Schedule an Appointment with Dr. Rodgers
Need help coping with eczema flares in yourself or your children? Consult the medical dermatology and pediatric dermatology experts at Rodgers Dermatology for fast relief.
Request an appointment online or give us a call at 972-808-5196 to speak with our friendly, welcoming staff about your skin concerns. We look forward to providing a personalized skin care plan to help you combat atopic dermatitis.